
Highlighted Publications

A high-performance genetically encoded sensor for cellular imaging of PKC activity in vivo
Nature Communications | 2025 July 10
Yahiro T, Bayless-Edwards L, Jones JA, Zhuo Y, Ma L, Qin M, Mao T†, Zhong H†
Neuromodulators impose powerful control over brain function via their regulation of intracellular signaling through G-protein coupled receptors. In contrast to those of Gs and Gi pathways, in vivo imaging of the signaling events downstream of Gq-coupled receptors remains challenging. Here, we introduce CKAR3, a genetically encoded fluorescence lifetime sensor that reports the activity of protein kinase C (PKC), a major downstream effector of the Gq pathway. CKAR3 exhibits a lifetime dynamic range 5-fold larger than any existing PKC sensor. It specifically detects PKC phosphorylation with seconds kinetics without perturbing neuronal functions. In vivo two-photon lifetime imaging of CKAR3 reveals tonic PKC activity in cortical neurons. Animal locomotion elicits robust PKC activity in sparse neuronal ensembles in the motor cortex. Both basal and locomotion-elicited PKC activities are in part mediated by muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Overall, CKAR3 enables interrogation of Gq signaling dynamics mediated by PKC in behaving animals.
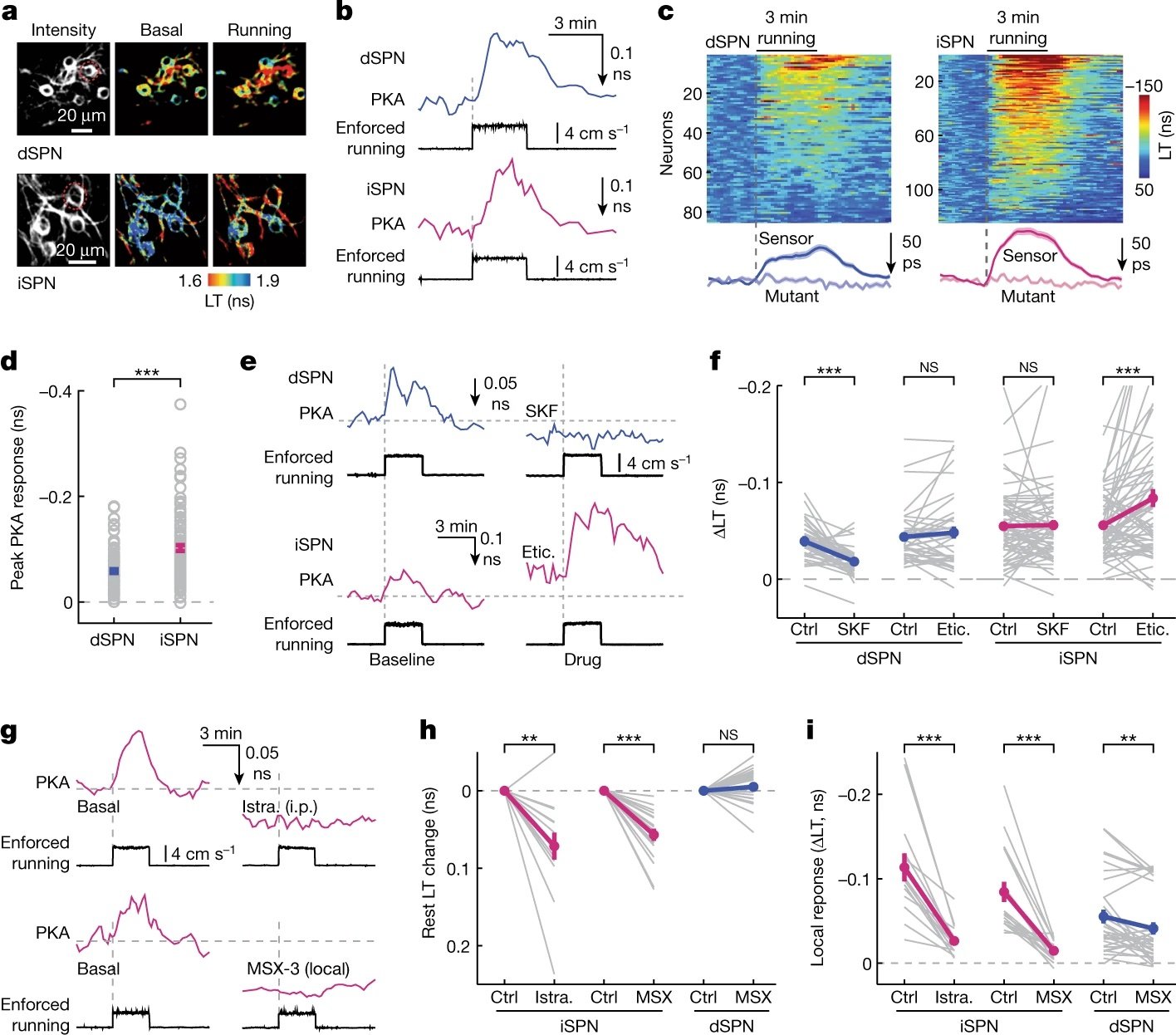
Locomotion activates PKA through dopamine and adenosine in striatal neurons
Nature | 2022 Nov 09
Ma L, Day-Cooney J, Benavides OJ, Muniak MA, Qin M, Ding JB, Mao T, Zhong H†
A novel FRET-based cAMP sensor is presented that was designed for in vivo imaging in awake behaving mice. The sensor is characterized in vitro and in vivo and used to define a heterogenous population of cells in the somatosensory cortex that either upregulate or downregulate cAMP in response to enforced running.

Sensitive genetically encoded sensors for population and subcellular imaging of cAMP in vivo
Nature Methods | 2022 Oct 27
Massengill CI*, Bayless-Edwards L*, Ceballos CC, Cebul ER, Cahill J, Bharadwaj A, Wilson E, Qin M, Whorton MR, Baconguis I, Ye B, Mao T†, Zhong H†
A novel FRET-based cAMP sensor is presented that was designed for in vivo imaging in awake behaving mice. The sensor is characterized in vitro and in vivo and used to define a heterogenous population of cells in the somatosensory cortex that either upregulate or downregulate cAMP in response to enforced running.
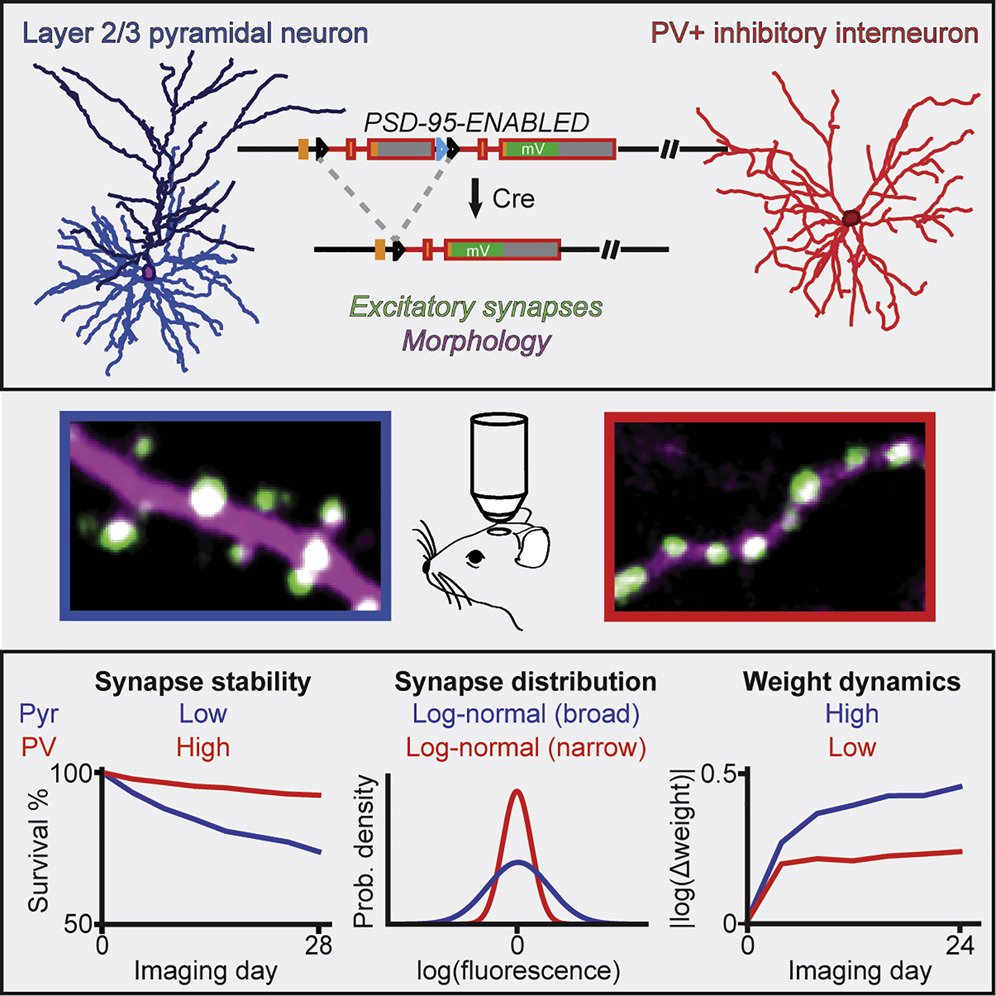
Distinct in vivo dynamics of excitatory synapses onto cortical pyramidal neurons and parvalbumin-positive interneurons
Cell Reports | 2021 Jul 30
Melander JB*, Nayebi A*, Jongbloets BC, Fortin DA, Qin M, Ganguli S†, Mao T†, Zhong H†
This study compares the synaptic properties of parvalbumin interneurons and pyramidal neurons.

Genetically encoded sensors towards imaging cAMP and PKA activity in vivo
Journal of Neuroscience Methods | 2021 Jul 31
Massengill CI, Day-Cooney J, Mao T, Zhong H†
Here we review the existing literature around in vivo fluorescent sensing of PKA and cAMP activity.

High-fidelity, efficient, and reversible labeling of endogenous proteins using CRISPR-based designer exon insertion
eLife | 2021 Jun 08
Zhong H†, Ceballos CC, Massengill CI, Muniak MA, Ma L, Qin M, Petrie SK, Mao T
Here, we describe a method called CRISPR-mediated insertion of exon (CRISPIE) that can precisely and reversibly label endogenous proteins using CRISPR/Cas9-based editing.

Visualizing Protein Kinase A Activity In Head-fixed Behaving Mice Using In Vivo Two-photon Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy
Journal of Visualized Experiments | 2019 Jun 07
Jongbloets BC*†, Ma L*, Mao T, Zhong H†
A procedure is presented to visualize protein kinase A activities in head-fixed, behaving mice. Two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy is used to visualize PKA activities in vivo during enforced locomotion.

Synapse-specific opioid modulation of thalamo-cortico-striatal circuits
eLife | 2019 May 17
Birdsong WT*†, Jongbloets BC*, Engeln KA, Wang D, Scherrer G, Mao T†
This study examined opioid actions on glutamate transmission between these brain regions in mouse. These results suggest that opioid effects on pain and reward may be shaped by the relative selectivity of opioid drugs to the specific circuit components.

A Highly Sensitive A-Kinase Activity Reporter for Imaging Neuromodulatory Events in Awake Mice
Neuron | 2018 Aug 09
Ma L*, Jongbloets BC*, Xiong WH*, Melander JB, Qin M, Lameyer TJ, Harrison MF, Zemelman BV, Mao T†, Zhong H†
Here, we developed a PKA sensor, tAKARα, which enables detection of physiologically relevant activity and interrogation of neuromodulation-induced PKA-signaling in awake animals.
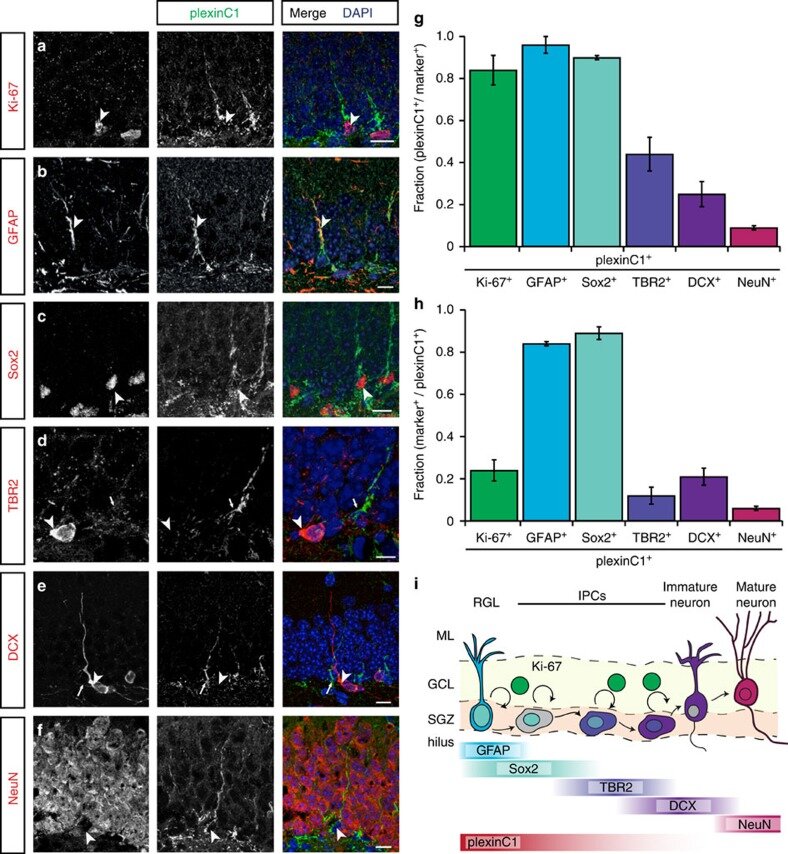
Stage-specific functions of Semaphorin7A during adult hippocampal neurogenesis rely on distinct receptors
Nature Communications | 2017 Mar 10
Jongbloets BC*, Lemstra S*, Schellino R, Broekhoven MH, Parkash J, Hellemons AJ, Mao T, Giacobini P, van Praag H, De Marchis S, Ramakers GM, Pasterkamp RJ†

A comprehensive excitatory input map of the striatum reveals novel functional organization
eLife | 2016 Nov 28
Hunnicutt BJ, Jongbloets BC, Birdsong WT, Gertz KJ, Zhong H, Mao T†
This study presents a comprehensive map of the excitatory inputs to the mouse striatum. The input patterns reveal boundaries between the known striatal domains The complete thalamo-cortico-striatal loop is also presented.

Live Imaging of Endogenous PSD-95 Using ENABLED: A Conditional Strategy to Fluorescently Label Endogenous Proteins
Journal of Neuroscience | 2014 Dec 10
Fortin DA, Tillo SE, Yang G, Rah JC, Melander JB, Bai S, Soler-Cedeño O, Qin M, Zemelman BV, Guo C, Mao T†, Zhong H†
Here, we describe a conditional mouse genetic strategy termed endogenous labeling via exon duplication (ENABLED), which can be used to fluorescently label endogenous proteins with near ideal properties in all neurons, a sparse subset of neurons, or specific neuronal subtypes.

A comprehensive thalamocortical projection map at the mesoscopic level
Nature Neuroscience | 2014 Aug 03
Hunnicutt BJ, Long BR, Kusefoglu D, Gertz KJ, Zhong H†, Mao T†
We employed a systematic, high-throughput viral approach to visualize thalamocortical axons with high sensitivity. We then developed algorithms to directly compare injection and projection information across animals and constructed a comprehensive map of thalamocortical projections.
